Bactria, to me, is Alexander-country, the lands of Central Asia where he spent two years of his life in 228 and 227 BC. The exceptional exhibition “Afghanistan, hidden treasures from the National
Museum, Kabul” covers this period and is presently traveling worldwide. It centers on four excavation sites covering roughly 2,500 years, i.e., from two thousand BC to the third century AD.
[Map from National Geographic showing Alexander's Route]
I knew French and Russian archaeologists had been working in the area for years, entrusting their treasures to the National Museum in Kabul. That is till 1979 when the troops of the USSR invaded Afghanistan. Archaeological diggings by Frenchman Paul Bernard at Ai-Khanoum, for instance, had to be interrupted abruptly, and when he returned to the site recently, it was thoroughly plundered and destroyed. Most damages were, however, done a few years later when the Taliban considered it their duty to obliterate every image of people wherever they found it: on frescoes, mosaics, paintings, reliefs, or statues. We all have witnessed what happened to the giant Buddha statues in Bamyan. Still, not many people know that the Museum of Kabul was one heap of rubble after the Taliban had thoroughly ravaged it – a frightening experience! A precious heritage that survived for centuries is being totally destroyed with just one single blow!
To use the old name, Bactria is located in Central Asia right on the crossroads of old caravan routes, later the Silk Road, the meeting point of all trade routes between East and West. It is not surprising that Alexander the Great put so much time and effort into the conquest of this area, for it meant not only a way to secure his back while heading for India but also an economic asset precisely because of the geographic location of Bactria. His marriage with Roxana, the local chief's daughter, was, after all, a high political move rather than real or impulsive love, as some suggest. Who knows?

The first objects I encounter as I enter the exhibition are three statues from the Musée Guimet in Paris, dating from Buddhist times but showing a definite Hellenistic influence. You can’t miss them; the way they are presented in the floodlights against a black background instantly gives you a taste of what to expect. This tremendous high relief of a Genius with Flowers from the 4th-5th century AD was found in the Buddhist monastery of Hadda in remote northern Afghanistan, yet still magnificently Hellenistic.
At a right angle, right in front of me, stands a showcase filled with one hundred Buddhist heads, sorted by size, i.e., the smaller ones on the lower steps and the bigger ones at the top. It is a fascinating group, for all the heads are different, and as I take a closer look at each and every one of them, either at eye level or from the side, I see how they stare back at me or ignore me, looking away in an absent glance. I take my time to inspect and admire each face, some more Hellenistic than others, with a more elongated or rounder face, longer ears, closed eyelids, or just peeping at us visitors. All in all, an amazing group!
From here, the way leads to the movie theater, where this French documentary is shown about their exploration and excavations
in the magnificent Afghan landscape. It is well documented with clear maps and
a captivating view behind the scenes – absolutely worth watching.
The oldest finds (2,000 BC) come from Tepe Fullol. There are only a handful of gold bowls and beakers made of thinly beaten gold that somehow reminds me of old Mycenae and the death mask of Agamemnon. Archaeologists disagree about the origins of this form of art, and the link to other cultures remains obscure. To complicate things, most of the treasures had disappeared, first because the gold was split up between the local tribal chiefs of Northern Afghanistan when it was discovered, and secondly, because the entire collection at the Museum of Kabul fell apart. These pieces are a little out of the way. That is unfortunate, for they deserve better after being hidden for four thousand years, don’t they?

The section about Ai-Khanoum is the most important one, at least in my eyes, for it is the reason for my visit, as this city was built in the wake of Alexander the Great’s conquest of the area in 328-327 BC. I am very much impressed by the idea of discovering this Hellenistic city at the banks of the Amu Daria River (modern Oxus River),
complete with a Gymnasium, Citadel, Theater, and temples. It is not as evident as it would seem! The Greeks even built a Palace here. It is unlike anything else, for they never had a king to build it for. This one is based on the Persian model but decorated in Greek style with monumental Corinthian capitals on top of the columns and flat roofs with the so-called antefix decorations at the edge. A capital and several antefixes are on display here, together with objects like a water jet in the shape of a theatrical mask, a couple of sundials (which I didn’t expect to find here at all), a Hellenistic Hermes pillar of high quality from the Gymnasium; a face of either a man or a woman; bronze decorative elements; etc.

Eye-catcher is the Disk of Cybele from the 3rd century BC made of gilded silver picturing the goddess Cybele on a chariot in Greek style mixed with several eastern influences featuring the fire altar and Helios.
What excites me is the stone pedestal bearing the Delphic precepts. This wisdom comes from 5th century Delphi and teaches us something along the lines of “As a child, learn good manners. As a young man, learn to control your passions. In middle age, be just. In old age, give good advice. When you die, do so without regret.” Can you imagine the impact of this old text, this old wisdom that traveled from Greece to resurface unexpectedly 2,500 years later at the very edge of the desert steppes? That leaves me utterly speechless for a while!
Next comes the collection from Begram, a small town north of Kabul. In the years before WWII, two sealed chambers were uncovered, still containing their treasures of ivory furniture from India, plaster medallions, and, most strikingly, an extensive collection of glasswork of Hellenistic origin. Here too, each archaeologist seems to have their own theory of whether these chambers were set up as storage areas (since all the ivory was put together, and so was all the bronze and all the glass), as religious offerings, or maybe this is a hidden treasure.
In any case, the glasswork alone is absolutely fabulous and unique in shape, color, and decoration. There are, for instance, these three goblets (they look more like vases to me, so tall). The countless pieces have been glued back together, but just by looking at the colors of these fishing and hunting scenes, you would swear they were painted only yesterday – so vivid and lively! Now try to imagine the impact of such a find, for these drinking beakers were produced in Alexandria in the first century AD and traveled all the way from Egypt to Kabul.
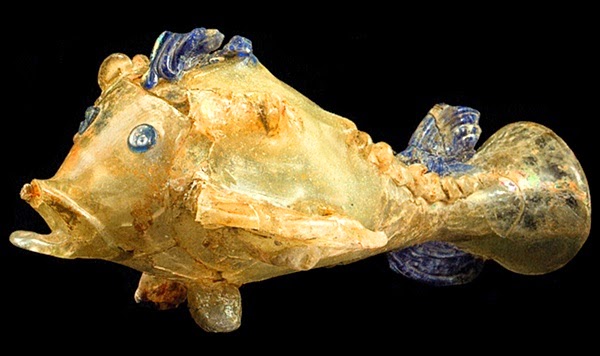
You have to admit that you are looking at something very exceptional. We all know there was an active exchange of goods in antiquity, and it comes to us like a simple statement from a history book, but here you are faced with the very product of such trade! I keep staring at this glasswork with wide-open eyes. Wow! Next to these painted glasses are a couple of glass drinking goblets or vases in the shape of fish, blue and off-white, with shiny eyes and sharp fins. I’ve never seen anything like this. There are glass-blown vases with honeycomb motives or wrapped in a net of glass lace; an elegant black glass vase with a high handle next to a translucent one covered with designs applied with gold leaf; for me, an unprecedented variety of delicate, colored, and painted glass that makes the cut-crystal bowl look rather primitive and dull. Amazing!
In another showcase, all the ivory artifacts have been brought together.

These objects from the first century AD originally all
come from India
but again are drenched in a Hellenistic sauce. Unique is the ivory River
Goddesses approximately 45
cm high, clearly from a Buddhist background, among the
exquisite openwork ivory panels showing Indian ladies in exotic gardens with
fountains and temple-like buildings, a few monster figures, etc. Strange is the
odd-shaped earthenware jar with blue-green glaze representing a bird-woman, for
I cannot tie this style or shape to anything I have seen before.
The bronze artifacts somehow don’t add anything
new. I only remember the cute figurine of Amor carrying a lamp and the
young rider who seems to refer to Alexander the Great because of the way
he is sitting on the horse that is lost from underneath him.
I stop to admire the row of plaster medallions,
each about 15 cm
in diameter, also dating from the first century AD. They look like oversized molds for the production
of coins but were used to create the bottom motives for silver plates and
goblets as the silver was poured and hammered around these molds. There are a
few striking designs, like the Winged Amor or the high relief of a
youth. Just imagine these portraits staring back at you from the bottom of your
silver goblet filled with water or wine. I certainly would love to give this a
try, wouldn’t you?
Finally, there is the gold treasure from Tillya
Tepe, a tomb hill just outside the Greek Bactrian city of Emshi-Tepe
in the oasis of Sherberghan. The content of these six tombs was barely
rescued when the Soviet Union entered Afghanistan in 1979, and it was
safely transferred to the Museum in Kabul. There was a seventh tomb on that
hill at the Turkmenistan border, but Viktor Sarianidi, the Russian
archaeologist who had led these excavations together with his Afghan colleagues, ran out of time, and when he recently returned, the tomb had been thoroughly
plundered. Such a shame! Luckily for us, Sarianidi managed to travel to
the Museum of Kabul in the 1980s in order to take pictures of all
20,000 excavated objects, and he published an impressive book. So at least we
know exactly what was found at Tillya Tepe.
What followed were uncertain times for the art
world, and we owe it to a handful of brave Afghans that this treasure was
rescued, safely locked away in the vaults of the Presidential Palace.
They managed to keep the place a secret. The Museum itself has suffered
a great deal from the civil wars as it was repeatedly plundered and artifacts
were stolen, and in 1994 it was hit by a rocket setting it on fire. How
dreadful! The worst, however, was still to come when in 2001, the Taliban decided
not only to destroy the huge Buddha statues at Bamyan but also to
annihilate the 2,500 statues and reliefs of the Museum. We had to wait
till 2004 when the government of Afghanistan
decided that the situation was safe enough to bring the gold treasures out in
the open again, but as the Museum in Kabul could not shelter this precious
collection yet, they contacted the Musée Guimet in Paris. Together they agreed to send
these rich finds on a traveling tour. After Paris
and Turin (Italy),
the collection can presently be seen in Amsterdam,
moved on to the United States, and is now touring Australia.
The tombs are beautifully presented in high
rectangular boxes covered with a glass plate showing the contours of the
deceased with underneath each piece of jewelry in its original place. They
unearthed one warrior and five women, the man lying at the top of the hill
between the two most beautifully dressed women, the other three women being
found on the hillside, which should have looked like a kurgan according
to the nomads’ rituals.
This part of the exhibition clearly states that
Northern Afghanistan was the melting pot of different cultures where the
influence of China and Greece are
interwoven with the lifestyle of the steppe people. Each tomb is an exploration
by itself, where all kinds of artifacts of different origins keep each other
company in breathtaking harmony.

Of course, they all have gold bracelets and anklets
inlaid or not with semi-precious stones, but I notice how some women hold a
Chinese mirror, from the Han Dynasty apparently; gold pins with on top a
gold flower with open petals and vibrant pistils; hairpins as I know them from
Japanese geishas but executed in thin flaky gold and tiny pearls; a ring
engraved with an Athena figure and Greek inscription, and rings inlaid with
precious stones; ornaments for the neck of the robe laid out as a necklace made
of gold, turquoise, garnet, carnelian, and pyrite; gold earrings preferably
inlaid with turquoise; pendants like those of the Dragon Master with
turquoise, garnet, lapis-lazuli, carnelian and pearls in a rare symbiosis of
Greek, Indian and Chinese elements; a set of gold clasps showing Amor riding
a dolphin with turquoise and mother of pearl; even gold foot soles!
The warrior, supposedly a prince, carries an iron
dagger with gold covered handle depicting animals and inlaid with turquoise.
His belt made of braided goldthread-strings connecting nine gold medallions
showing a warrior riding a lion is an exceptional masterpiece. His head rested
on a phial, a plate used for offerings, made of pure gold and measuring nothing
less than 23 cm
in diameter!
The list seems endless, for besides the most striking objects, the collection contains numerous coins, pendants, and various decoration items. As the most recent coin found in these tombs is that of Emperor Tiberius (who ruled from 14 to 37 AD), they could be dated with certainty to the first century AD. We see a true amalgamation of art from the steppes (I would personally call this Scythian art), Greek, Indian, and Chinese art.

I am terribly excited to finally catch up with the Aphrodite of Bactria, a five centimeters high gold appliqué inlaid with turquoise. I know the piece from pictures and references, but here she is. I go down on my knees to look closer; for an instant, she is mine alone. The piece de resistance, however, seems to be the gold crown with gold spangles and flowers. It is, in fact, a travel crown that can be taken apart as it consists of five separate pieces mounted around a tiny stem holding flattened branches that fit into the band of the crown itself. The spangles gently shake as people walk by, so imagine this crown in the open steppe where the wind can play freely with every tiny detail! A true gem!

It is still unclear to which nomad tribes the tombs of Tillya Tepe belong and how far this melting pot of civilizations reached out. Generally, these steppe people came from northwestern China or Parthia (now part of Iran and Turkmenistan), but who knows? Further investigations will tell us. For now, we have to accept that this territory is vast, for we have jade from China, garnets from India, turquoise from eastern Iran, and lapis lazuli from the mines of Badakhshan (today’s Afghanistan), all found together in this area. And yet we have not mentioned the traders and artists who were constantly moving between China, India, and the Roman Empire to produce these beautiful artifacts. It’s a small world – or is it not so small after all?
Anyway, I am convinced that this wide exchange of art and knowledge would not have been possible without Alexander the Great conquering these territories and organizing his Empire as he did.

















No comments:
Post a Comment